Connect your App to the Outside World
On Unikraft Cloud, all of your instances, when created, are given a private IP address and private FQDN, so you can immediately (inter)connect them. Connecting them to the Internet is done through a service: you simply create a service and attach your instance(s) to it.
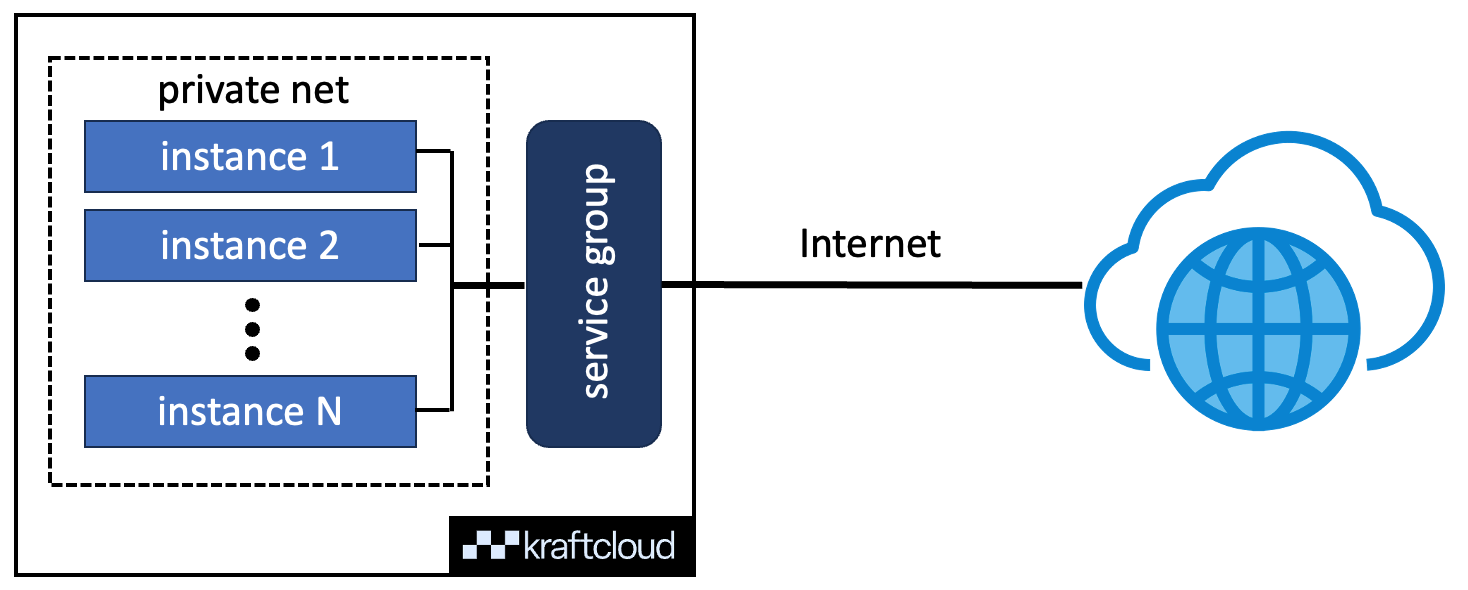
The following diagram illustrates the concept:
If you’ve used the kraft cloud deploy command, you may have noticed that part of the output lists a service, e.g.:
├─ service: frosty-sky-vz8kwsmSince kraft cloud deploy is a single command to have a service deployed, it automatically creates a service and attaches the instance just created to it.
The rest of this guide shows how to create a service first, and then use kraft cloud deploy to create and attach instances to it.
First, let’s start by creating a new service; we can do so by using the kraft cloud service command:
kraft cloud service create --name my-service 443:8080/http+tlsHere we created a new service called my-service listening on port 443.
Unikraft Cloud will terminate TLS and send HTTP to port 8080, i.e., this example will assume that the app will open port 8080.
Now let’s use kraft cloud deploy with the --service flag to ask kraft to attach the instance to our my-service service.
For example, if we take the Go web server guide (see all guides here):
git clone https://github.com/unikraft-cloud/examplescd examples/http-go1.21/kraft cloud deploy --service my-service .This will create a new Go web server instance and immediately attach it to the my-service service.
The output shows the instance URL and other details:
[●] Deployed successfully! │ ├────────── name: http-go121-fkt1x ├────────── uuid: 858da707-1851-46cb-9667-05b951471222 ├───────── state: running ├─────────── url: https://my-service-rrtckyyi.fra0.kraft.host ├───────── image: http-go121@sha256:4d536236d226781874c3ad930dbc936c4f407aa3483a1f8e961ba63a7a72c78d ├───── boot time: 17.14 ms ├──────── memory: 128 MiB ├─────── service: my-service ├── private fqdn: http-go121-fkt1x.internal ├──── private ip: 172.16.6.6 └────────── args: /serverIn this case, the instance name is http-go121-fkt1x and the URL is https://my-service-rrtckyyi.fra0.kraft.host.
They are different for each run.
Use curl to query the Go web server from the Internet:
curl https://my-service-rrtckyyi.fra0.kraft.hosthello, world!That’s it!
In the end, if you want to remove a service, use:
kraft cloud service remove my-serviceLearn More
- The
kraft cloudCLI reference, and in particular the services sub-command - Unikraft Cloud’s REST API reference, and in particular the section on services